A Two-Dimensional MoS2 Catalysis Transistor by Solid-State Ion Gating Manipulation and Adjustment (SIGMA)
Abstract
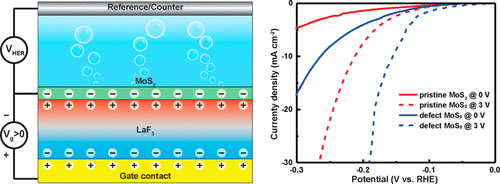
A variety of methods including tuning chemical compositions, structures, crystallinity, defects and strain, and electrochemical intercalation have been demonstrated to enhance the catalytic activity. However, none of these tuning methods provide direct dynamical control during catalytic reactions. Here we propose a new method to tune the activity of catalysts through solid-state ion gating manipulation and adjustment (SIGMA) using a catalysis transistor. SIGMA can electrostatically dope the surface of catalysts with a high electron concentration over 5 $times$ 1013 cm-2 and thus modulate both the chemical potential of the reaction intermediates and their electrical conductivity. The hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) on both pristine and defective MoS2 were investigated as model reactions. Our theoretical and experimental results show that the overpotential at 10 mA/cm2 and Tafel slope can be in situ, continuously, dynamically, and reversibly tuned over 100 mV and around 100 mV/dec, respectively.