Atomistic simulations of heterogeneous electrocatalysis at the center of sustainable carbon feedstocks
Abstract
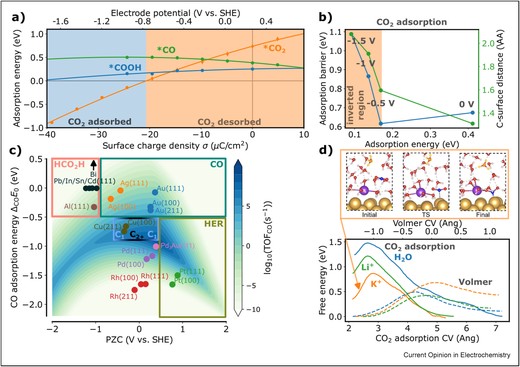
In the face of global warming, the electrochemical valorization of sustainable carbon feedstocks has a high potential to advance green chemistry and promote environmentally friendly practice.Computational simulations have become indispensable in shedding light on specific aspects of electrocatalytic processes. Modern techniques incorporate the effects of the electric double layer, enhancing their ability to model realistic systems. This review provides an overview and critical discussion of the latest developments. Density functional theory remains the preferred method for studying electrode reactions and interfacial effects on stationary or short-time scales. In contrast, force field-based methods excel at providing a full statistical sampling of solid–liquid interfaces. Machine learning techniques represent a critical step toward desirable multipurpose, multi-scale methods that deliver high accuracy and coupling across multiple time and length scales.