Cation effects on electrocatalytic reduction processes at the example of the hydrogen evolution reaction
Abstract
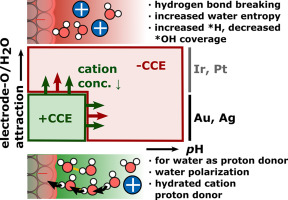
Cation effects provide invaluable insights about electrochemistry. In this review, I discuss them with a main focus on the hydrogen evolution reaction and a summary of recent insitu spectroscopic and electrochemical measurements as well as advanced computational simulation results conducted at varying cation identities, concentrations and pH. According to these works, the interfacial cation concentration is the main descriptor to explain cation and pH effects. The detailed mechanism (such as e.g. water polarization, water structure changes, field-stabilization of intermediates) depends strongly on potential, pH, oxophilicity of the electrode or the nature of the rate-limiting step and proton donor. With growing convergence in this field, cation effects remain a highly challenging as promising topic for research.